lLouie
Student
- Jun 19, 2024
- 72
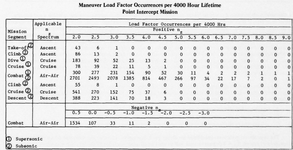
- Subsonic Flight: Fatigue is primarily dominated by high-cycle fatigue (HCF) due to repetitive low-stress loading. The absence of extreme thermal fluctuations reduces the impact of thermal fatigue, leading to a longer material lifespan.
- Supersonic Flight: More severe low-cycle fatigue (LCF) occurs due to rapid pressure fluctuations from shock waves. Additionally, aerodynamic heating causes thermal fatigue and creep, accelerating material degradation. Therefore, high-temperature-resistant materials like titanium alloys and composite materials are crucial for durability.
I came across AGARD while researching. The fatigue behavior will be different between subsonic and supersonic flight. So, what kind of aerodynamic loading will occur when transitioning from subsonic to supersonic? For fatigue analysis, both subsonic and supersonic conditions need to be considered.
I am curious about your opinion on this and whether there are any relevant sources available. Could you share any references on this topic?