Wfg42438
Electrical
- Apr 10, 2017
- 70
Hello Everyone,
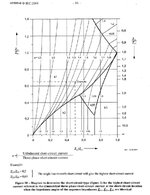
In section 7.2 of the IEEE 399 book there is some discussion about 3Ph faults vs LG fault for protective device duty analysis. (see attached image)

Typically its most common to focus on the 3Ph faults however for the special condition where LG faults results are larger than 3Ph the following questions come to mind:
In the IEEE 399 we are told MV and HV CBs have 15% higher interrupting ratings for LG faults.
Can someone elaborate on following:
1. By this statement does that mean the breaker is somehow designed to have a 15% higher int. rating for LG faults exclusively or am i misinterpreting the text?
2. Based on item 1 does that mean data sheets provide an additional LG int rating and if so, is there a sample anyone can share?
3. The section touches on MV and HV CBs what about all other devices?
For example under the same conditon where LG is worst case whats to be done for Bus bars, Fuses, LVCBs, etc?
Has anyone seen any guidance for such cases or is there some practical reason IEEE 399 does not mention other equipment for such special cases?
In section 7.2 of the IEEE 399 book there is some discussion about 3Ph faults vs LG fault for protective device duty analysis. (see attached image)

Typically its most common to focus on the 3Ph faults however for the special condition where LG faults results are larger than 3Ph the following questions come to mind:
In the IEEE 399 we are told MV and HV CBs have 15% higher interrupting ratings for LG faults.
Can someone elaborate on following:
1. By this statement does that mean the breaker is somehow designed to have a 15% higher int. rating for LG faults exclusively or am i misinterpreting the text?
2. Based on item 1 does that mean data sheets provide an additional LG int rating and if so, is there a sample anyone can share?
3. The section touches on MV and HV CBs what about all other devices?
For example under the same conditon where LG is worst case whats to be done for Bus bars, Fuses, LVCBs, etc?
Has anyone seen any guidance for such cases or is there some practical reason IEEE 399 does not mention other equipment for such special cases?