Navigation
Install the app
How to install the app on iOS
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
More options
Style variation
-
Congratulations MintJulep on being selected by the Eng-Tips community for having the most helpful posts in the forums last week. Way to Go!
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Pneumatic Differentiator
- Thread starter Green 123
- Start date
- Status
- Not open for further replies.
TugboatEng
Marine/Ocean
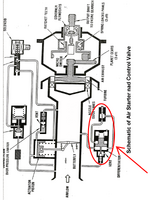
It has a piston and spring that push down on a ball. Air pressure down stream of the butterfly lifts the piston off the ball. The rate the piston moves is slowed by a needle valve. When the ball lifts it vents the actuator piston which closes the butterfly.
In short terms, it regulates the air pressure at the nozzle guide vanes.
In short terms, it regulates the air pressure at the nozzle guide vanes.
- Thread starter
- #3
much obligedIt has a piston and spring that push down on a ball. Air pressure down stream of the butterfly lifts the piston off the ball. The rate the piston moves is slowed by a needle valve. When the ball lifts it vents the actuator piston which closes the butterfly.
In short terms, it regulates the air pressure at the nozzle guide vanes.
LittleInch
Petroleum
There are a series of complex looking systems here.
The higher pressure air comes from upstream the valve.
When the solenoid acts it directs air to the top of the piston moving the valve. This supply has what looks like an over speed regulator so if the air flow moves too fast it moves the piston closing off t h e air supply.
The supply to the piston is also regulated by that device which seem to have a slow acting vent relief. It's precise mechanism and how it interacts with all the other bits is opaque without a better description of the operation, pressures and flows.
The higher pressure air comes from upstream the valve.
When the solenoid acts it directs air to the top of the piston moving the valve. This supply has what looks like an over speed regulator so if the air flow moves too fast it moves the piston closing off t h e air supply.
The supply to the piston is also regulated by that device which seem to have a slow acting vent relief. It's precise mechanism and how it interacts with all the other bits is opaque without a better description of the operation, pressures and flows.
- Thread starter
- #5
- Thread starter
- #6
The air control valve controls the flow and the pressure of the air from the air ducting to the air starter motor.There are a series of complex looking systems here.
The higher pressure air comes from upstream the valve.
When the solenoid acts it directs air to the top of the piston moving the valve. This supply has what looks like an over speed regulator so if the air flow moves too fast it moves the piston closing off t h e air supply.
The supply to the piston is also regulated by that device which seem to have a slow acting vent relief. It's precise mechanism and how it interacts with all the other bits is opaque without a better description of the operation, pressures and flows.
The butterfly valve is installed in the valve body and is operated with the actuator assembly. The position indicator switch is attached to valve body and operated with the butterfly valve shaft. The end of the butterfly valve shaft is square and comes through the position indicator switch. The two electrical connectors connect the solenoid and the position indicator switch to the control and indication system
When the electrical input is supplied, the solenoid is energised and opens an air port to the actuator. The actuator turns the butterfly valve to let the aiflow through to the air starter motor. The air control valve monitors the air pressure upstream and downstream of the butterfly valve. The actuator turns the butterfly to keep the downstream (outlet to the air starter motor) pressure constant. When the electrical input is stopped, the solenoid is deenergised and the air port is closed. The butterfly valve turns to the closed position.
The pushswitch on the ENGINE panel and the cut-out switch on the air starter motor, control the electrical input to the solenoid . The position switch sends an output to the contol and indication system
The butterfly valve can be opened and closed manually with a spanner on the square end of the shaft.
GregLocock
Automotive
In the steady state the pressure on each side of the piston is equal, but the vent by the base of the spring means that the net force on the piston from the gas, due to the difference in surface area, is resisted by the spring. This opens the ball valve, which allows the pressure on the piston on the butterfly to vent to atmosphere. The needle valve probably acts as a damper.
If the pressure on the tapping increases, the piston compresses the spring more, allowing the ball valve to open more, venting more air from the butterfly's piston, allowing it to move up and alter the angle of the butterfly.
At a guess...
If the pressure on the tapping increases, the piston compresses the spring more, allowing the ball valve to open more, venting more air from the butterfly's piston, allowing it to move up and alter the angle of the butterfly.
At a guess...
TugboatEng
Marine/Ocean
Green, do understand that the line that passes in proximity of the word butterfly is passing around that section and not sensing that section. Notice the gap in the black lines.
I don't know how the manual opening description contributes to this question.
I don't know how the manual opening description contributes to this question.
Last edited:
GregLocock
Automotive
Yes the rather puzzling layout drawing deterred me from answering initially, the line from the ball valve/vent to the top of the actuator piston is actually continuous. Funny old drawing.
TugboatEng
Marine/Ocean
I prefer this type of drawing to the ISO stuff. No symbols to memorize and it gives a more complete concept of operation.
- Thread starter
- #12
The upstream side of the differentiator is connected to the upper chamber of the actuator. The actuator controls the position of the butterfly valve. The actuator has two chambers, namely upper chamber and lower chamber. A spring inside the actuator makes the start control valve normally closed. The upper chamber gets air from the reference pressure regulator. A solenoid valve is electrically operated through the start selector on the ENGINE panel. The reference pressure regulator controls the air pressure for the upper chamber. I suppose that the differentiator controls the rate of movement of the butterfly valve however I don’t know how it does. do you concur with me?Green, do understand that the line that passes in proximity of the word butterfly is passing around that section and not sensing that section. Notice the gap in the black lines.
I don't know how the manual opening description contributes to this question.
Last edited:
- Thread starter
- #13
The upstream side of the differentiator is connected to the upper chamber of the actuator. The actuator controls the position of the butterfly valve. The actuator has two chambers, namely upper chamber and lower chamber. A spring inside the actuator makes the start control valve normally closed. The upper chamber gets air from the reference pressure regulator. A solenoid valve is electrically operated through the start selector on the ENGINE panel. The reference pressure regulator controls the air pressure for the upper chamber. I suppose that the differentiator controls the rate of movement of the butterfly valve however I don’t know how it does. do you concur with me?Yes the rather puzzling layout drawing deterred me from answering initially, the line from the ball valve/vent to the top of the actuator piston is actually continuous. Funny old drawing.
Last edited:
GregLocock
Automotive
No, I think it controls the butterfly's position as the primary function. The needle valve probably acts to damp that motion.
- Thread starter
- #15
Ta muchlyNo, I think it controls the butterfly's position as the primary function. The needle valve probably acts to damp that motion.
- Thread starter
- #16
Does damping of flow through the needle valve cause slow variation of butterfly's position?No, I think it controls the butterfly's position as the primary function. The needle valve probably acts to damp that motion.
GregLocock
Automotive
Not in the steady state, it just affects the rate at which the butterfly can move. Hang on, bear in mind I've never seen one of these things, I'm just working from first principles.
- Thread starter
- #18
Much obligedNot in the steady state, it just affects the rate at which the butterfly can move. Hang on, bear in mind I've never seen one of these things, I'm just working from first principles.
Orange_kun
Mechanical
To me, it looks like the differentiator will act to limit the rate of change of pressure in the inlet. If inlet pressure tap rises too quickly, the screw adjust needle valve damps flow to the spring loaded side of the differentiator. This allows the pressure spike to move the piston (up, as shown) which lifts the ball off the seat, vents the actuator cylinder, and closes the butterfly valve partially. Valve closes partially, flow is throttled, pressure between butterfly and guide vanes drops.
I don't think it will govern the absolute pressures anywhere in the system, unless the screw valve is totally closed. But I would imagine it has the effect of making the inlet pressure to the turbine less variable. Any instant the nozzle guide vanes are taking more or less air than the butterfly is admitting, the differentiator will change the butterfly position, briefly.
Apologies if that's reiterating what GregLocock said. I think they stated what I inferred.
I don't think it will govern the absolute pressures anywhere in the system, unless the screw valve is totally closed. But I would imagine it has the effect of making the inlet pressure to the turbine less variable. Any instant the nozzle guide vanes are taking more or less air than the butterfly is admitting, the differentiator will change the butterfly position, briefly.
Apologies if that's reiterating what GregLocock said. I think they stated what I inferred.
- Status
- Not open for further replies.
Similar threads
- Locked
- Question
- Replies
- 2
- Views
- 405
- Locked
- Question
- Replies
- 65
- Views
- 3K
- Locked
- Question
- Replies
- 13
- Views
- 1K
- Locked
- Question
- Replies
- 14
- Views
- 722
- Locked
- Question
- Replies
- 22
- Views
- 1K